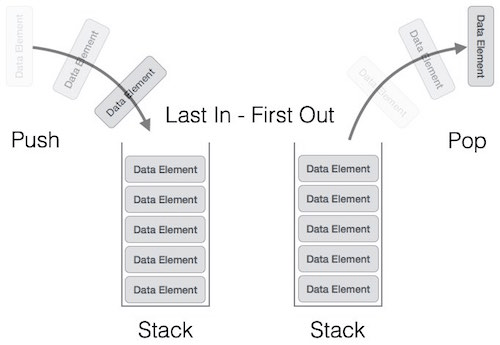
Stack is a linear data structure, which is collection of items of the same data type. Stack follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) fashion, where the last element inserted first will be popped out first.
Push and Pop only at one end
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Stack
{
int data;
struct Stack *next;
}*top = NULL;
void push(int x)
{
struct Stack *t = (struct Stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
if(t == NULL)
{
printf("Stack is Push");
}
else
{
t->data = x;
t->next = top;
top = t;
}
}
void pop()
{
struct Stack *t;
if(top == NULL)
{
printf("Stack is Empty\n");
}
else
{
t = top;
top = top->next;
free(t);
}
}
void Display()
{
struct Stack *t = top;
while(t)
{
printf("%d ", t->data);
t = t->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter the no. of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
push(arr[i]);
}
Display();
pop();
printf("\n");
Display();
}
Leave a comment