Linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Here each node stores the data and the address of the next node.
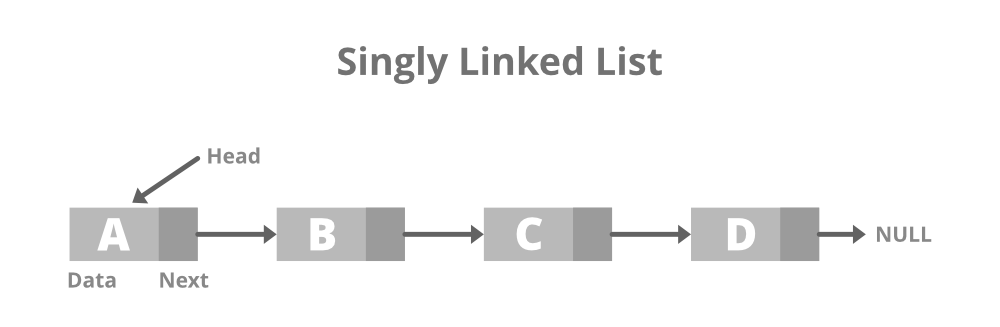
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}*first = NULL;
void create(int A[], int n)
{
struct Node *t, *last;
first = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
first->data = A[0];
first->next = NULL;
last = first;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
t = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
t->data = A[i];
t->next = NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
}
int count(struct Node *p)
{
int c = 0;
while(p)
{
c = c + 1;
p = p->next;
}
return c;
}
void Delete(struct Node *p, int pos)
{
struct Node *q = NULL;
if(pos < 1 || pos > count(p))
{
printf("Cannot perform Deletion");
}
if(pos == 1)
{
q = first;
first = first->next;
free(q);
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<pos-1; i++)
{
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Display(struct Node *p)
{
while(p)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
int IsSorted(struct Node *p)
{
int x = INT_MIN;
p = first;
while(p)
{
if(p->data < x)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
x = p->data;
p = p->next;
}
}
return 1;
}
void Reverse(struct Node *p)
{
int *A;
struct Node *q = p;
A = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*count(p));
int i=0;
while(q)
{
A[i] = q->data;
i++;
q = q->next;
}
q = p;
i--;
while(q)
{
q->data = A[i];
i--;
q = q->next;
}
}
void Reverse1(struct Node *p)
{
struct Node *q = NULL;
struct Node *r = NULL;
while(p)
{
r = q;
q = p;
p = p->next;
q->next = r;
}
first = q;
}
int main()
{
struct Node *p = first;
int A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int n = 10;
create(A, n);
printf("%d ", IsSorted(p));
printf("\n");
Delete(first, 4);
Display(first);
printf("\n");
Reverse(first);
Display(first);
Reverse1(first);
printf("\n");
Display(first);
}
Leave a comment