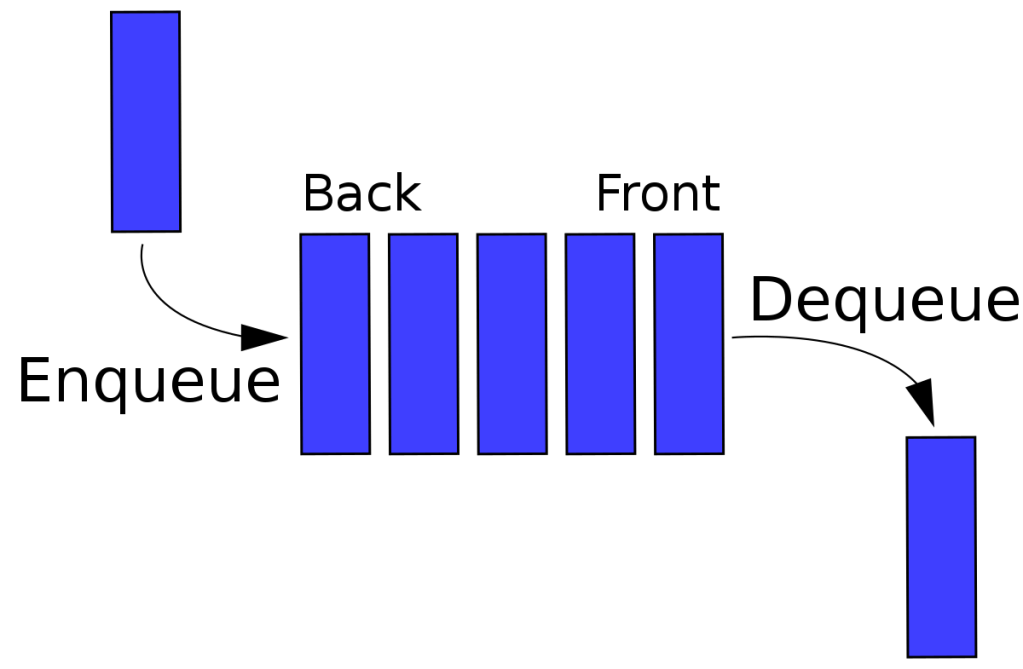
Queue is a linear data structure, which follows the First In First Out(FIFO) fashion. It is the collection of similar data types
Queue contains two pointers namely, *front , *rear. Before Inserting element into the Queue front pointer and rear pointer will be pointing to NULL. While Enqueuing an element in to the Queue front and rear pointers pointed to zero. And when the Second Element is enqueued, only rear pointer will be incremented.
Code in C:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Queue
{
int data;
struct Queue *next;
}*front = NULL, *rear = NULL;
void enqueue(int x)
{
struct Queue *t = (struct Queue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Queue));
if(t == NULL)
{
printf("Queue is Full");
}
else
{
t->data = x;
t->next = NULL;
if(front == NULL)
{
front = rear = t;
}
else
{
rear->next = t;
rear = t;
rear->next = NULL;
}
}
}
void dequeue()
{
struct Queue *t = (struct Queue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Queue));
if(front == NULL)
{
printf("Queue is Empty");
}
else
{
t = front;
front = front->next;
free(t);
}
}
void Display(struct Queue *p)
{
if(p)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
Display(p->next);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter the no. of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("Enter the %d element: ", i+1);
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
enqueue(arr[i]);
}
printf("Queue Elements are: ");
Display(front);
printf("\nAfter popping an element from the Queue: ");
Display(front);
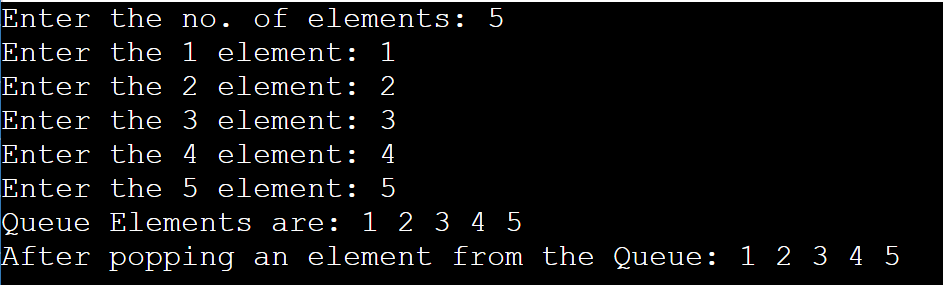
}Output:
Leave a comment