Binary Search Tree is a type of Binary Tree, where it follows some specific order in arranging the elements, In a binary search tree, the value of the left node should be less than the root node, the value of the right node should be greater than the root node. This rule is applied recursively to the left and right subtrees of the root.

In the above figure, we can observe that the root node is 40, and all the nodes of the left subtree are smaller than the root node, and all the nodes of the right subtree are greater than the root node.
Similarly, we can see the left child of root node is greater than its left child and smaller than its right child. So, it also satisfies the property of binary search tree. Therefore, we can say that the tree in the above image is a binary search tree.
Advantages of Binary Search Tree:
- Searching an element in the Binary search tree is easy as we always have a hint that which subtree has the desired element.
- As compared to array and linked lists, insertion and deletion operations are faster in BST.
Example of Creating Binary Search Tree:
Now, let’s see the creation of binary search tree using an example.
Suppose the data elements are – 45, 15, 79, 90, 10, 55, 12, 20, 50
- First, we have to insert 45 into the tree as the root of the tree.
- Then, read the next element; if it is smaller than the root node, insert it as the root of the left subtree, and move to the next element.
- Otherwise, if the element is larger than the root node, then insert it as the root of the right subtree.
Step-1: INSERT 45

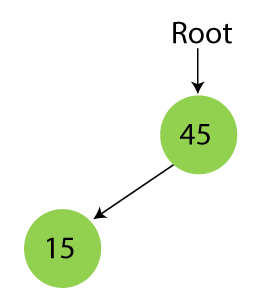
Step 2 – Insert 15
As 15 is smaller than 45, so insert it as the root node of the left subtree.
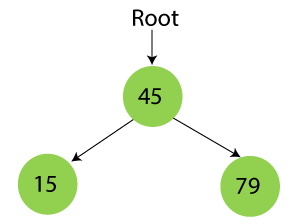
Step 3 – Insert 79
As 79 is greater than 45, so insert it as the root node of the right subtree.
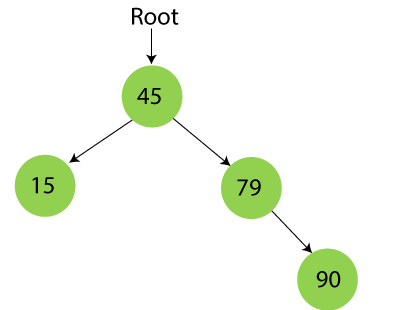
Step 4 – Insert 90
90 is greater than 45 and 79, so it will be inserted as the right subtree of 79
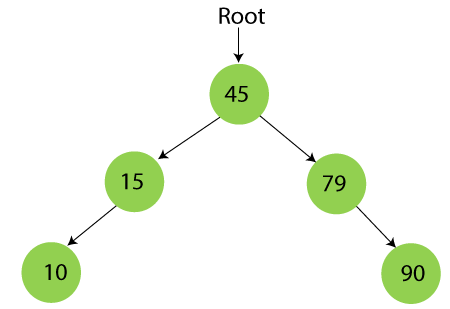
Step 5 – Insert 10
10 is smaller than 45 and 15, so it will be inserted as a left subtree of 15.
Step 6 – Insert 55
55 is larger than 45 and smaller than 79, so it will be inserted as the left subtree of 79.
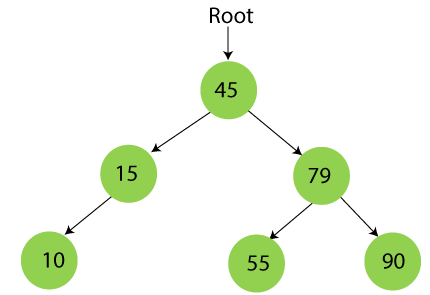
Step 7 – Insert 12
12 is smaller than 45 and 15 but greater than 10, so it will be inserted as the right subtree of 10.
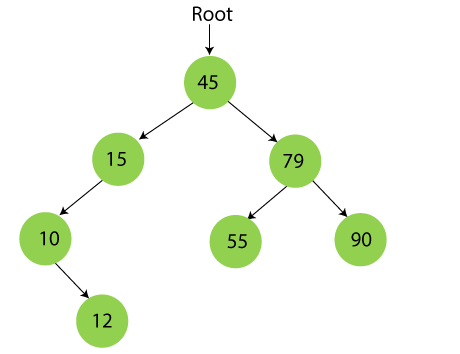
Step 8 – Insert 20
20 is smaller than 45 but greater than 15, so it will be inserted as the right subtree of 15.
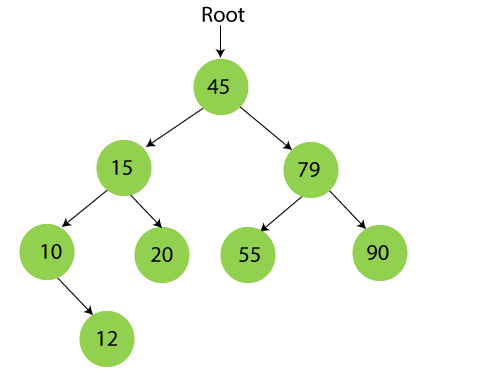
Step 9 – Insert 50
50 is greater than 45 but smaller than 79 and 55. So, it will be inserted as a left subtree of 55.
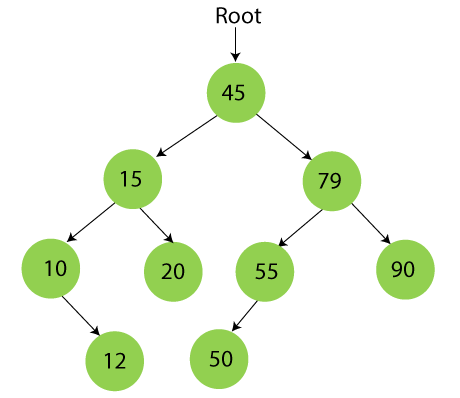
Now, the creation of binary search tree is completed.
Implementation of Binary Search Tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Tree
{
int data;
struct Tree *left;
struct Tree *right;
}*root = NULL;
void create(int x)
{
struct Tree *t = root;
struct Tree *r, *p;
if(root == NULL)
{
p = (struct Tree *)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
p->data = x;
p->left = p->right = NULL;
return;
}
while(t!=NULL)
{
r = t;
if(x > t->data)
{
t = t->right;
}
else if(x < t->data)
{
t = t->left;
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}
struct Tree *Rinsert(struct Tree *p, int x)
{
struct Tree *t = NULL;
if(p == NULL)
{
t = (struct Tree *)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));
t->data = x;
t->left = t->right = NULL;
return t;
}
if(x == p->data)
{
return p;
}
if(x < p->data)
{
p->left = Rinsert(p->left, x);
}
else if(x > p->data)
{
p->right = Rinsert(p->right, x);
}
return p;
}
void inorder(struct Tree *p)
{
if(p)
{
inorder(p->left);
printf("%d ", p->data);
inorder(p->right);
}
}
int Height(struct Tree *p)
{
int x,y;
if(p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
x = Height(p->left);
y = Height(p->right);
if(x>y)
{
return x+1;
}
else
{
return y+1;
}
}
struct Tree *Inpre(struct Tree *p)
{
while(p && p->right!=NULL)
{
p = p->right;
}
return p;
}
struct Tree *Insucc(struct Tree *p)
{
while(p && p->left!=NULL)
{
p = p->left;
}
return p;
}
struct Tree *Delete(struct Tree *p, int x)
{
struct Tree *q;
if(p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if(p->left == NULL && p->right == NULL)
{
if(p == root)
{
root = NULL;
}
free(p);
return NULL;
}
if(x < p->data)
{
p->left = Delete(p->left, x);
}
else if(x > p->data)
{
p->right = Delete(p->right, x);
}
else
{
if(Height(p->left) > Height(p->right))
{
q = Inpre(p->left);
p->data = q->data;
p->left = Delete(p->left, q->data);
}
else
{
q = Insucc(p->right);
p->data = q->data;
p->right = Delete(p->right, q->data);
}
}
return p;
}
int main()
{
struct Tree* temp;
int n;
printf("Enter the number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
root = Rinsert(root, arr[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
Rinsert(root, arr[i]);
}
inorder(root);
Delete(root, 7);
printf("\n");
inorder(root);
}
Leave a comment