SET OPERATIONS
Set operations are used to combine the results of two or more queries into a single result. The combined queries must return the same number of columns and compatible data types. The names of the corresponding columns can be different.
CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING TABLE
- CYCLING TABLE
| id | name | country |
| 1 | YZ | DE |
| 2 | ZG | DE |
| 3 | WT | PL |
- SKATING TABLE
| id | name | country |
| 1 | YK | DE |
| 2 | DF | DE |
| 3 | AK | PL |
UNION
The UNION operator is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements.
- Every
SELECTstatement withinUNIONmust have the same number of columns - The columns must also have similar data types
- The columns in every
SELECTstatement must also be in the same order

SYNTAX
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
WHERE condition
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2
WHERE condition;Example
This query displays German cyclists together with German skaters:
SELECT name FROM cycling
WHERE country = 'DE'
UNION
SELECT name FROM skating
WHERE country = 'DE';UNION ALL
The UNION operator selects only distinct values by default. To allow duplicate values, use UNION ALL:
SYNTAX
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
WHERE condition
UNION ALL
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2
WHERE conditionExample
SELECT name FROM cycling
WHERE country = 'DE'
UNION ALL
SELECT name FROM skating
WHERE country = 'DE';INTERSECT
The SQL INTERSECT clause/operator is used to combine two SELECT statements, but returns rows only from the first SELECT statement that are identical to a row in the second SELECT statement. This means INTERSECT returns only common rows returned by the two SELECT statements.
Just as with the UNION operator, the same rules apply when using the INTERSECT operator.
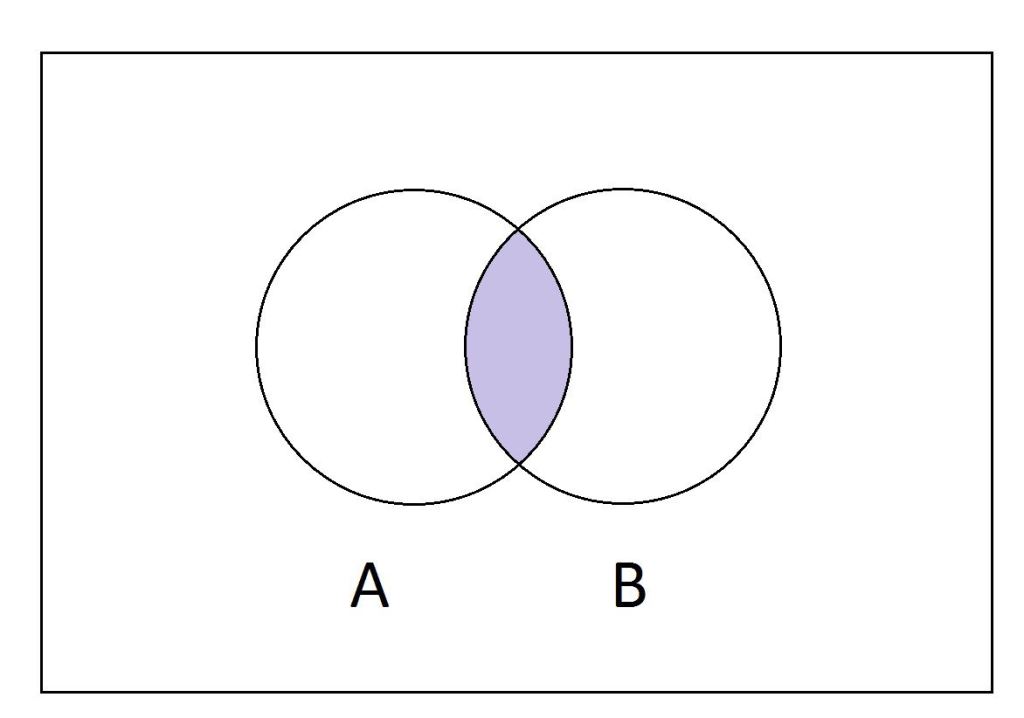
Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
WHERE condition
INTERSECT
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2
WHERE condition;Example
This query displays German cyclists who are also German skaters at the same time:
SELECT name FROM cycling
WHERE country = 'DE'
INTERSECT
SELECT name FROM skating
WHERE country = 'DE';EXCEPT
The SQL EXCEPT clause/operator is used to combine two SELECT statements and returns rows from the first SELECT statement that are not returned by the second SELECT statement. This means EXCEPT returns only rows, which are not available in the second SELECT statement.
Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
WHERE condition
EXCEPT
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2
WHERE condition;Example
This query displays German cyclists unless they are also German skaters at the same time:
SELECT name
FROM cycling
WHERE country = 'DE'
EXCEPT
SELECT name
FROM skating
WHERE country = 'DE';
Leave a comment