Linear regression is a widely used statistical technique that helps us explore the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. However, when applying linear regression, we need to consider certain assumptions to ensure the validity of our analysis. In this post, we will discuss five key assumptions in linear regression and also touch upon the process of outlier checking. So, let’s dive in!
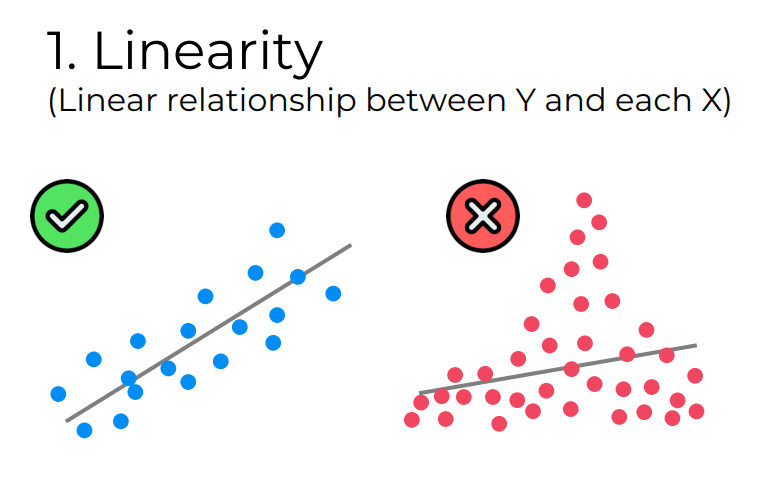
1. Linearity
The assumption of linearity suggests that the relationship between the dependent variable and each of the independent variables is linear. In other words, the effect of independent variables on the dependent variable is additive for linear regression to be appropriate.
To validate this assumption, practitioners often rely on scatterplots and residual plots, ensuring that the observed patterns align with a straight line.
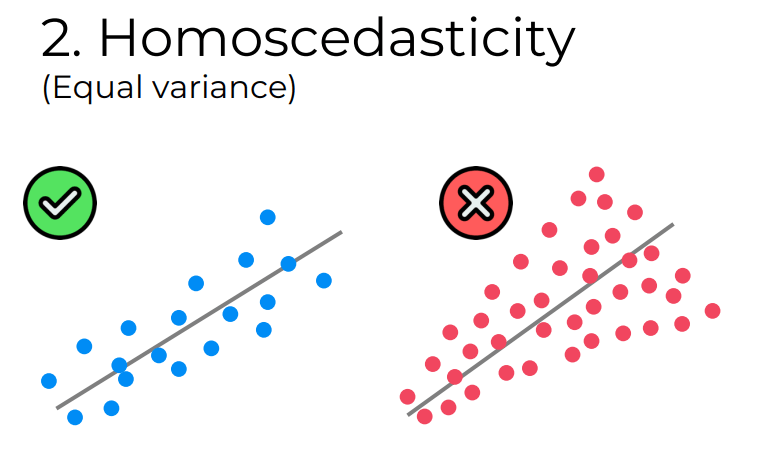
2. Homoscedasticity
Homoscedasticity assumes that the variance of the residuals (the differences between the observed and predicted values) is constant across all levels of the independent variables. This means that the spread of the residuals should not systematically change as we move along the independent variable(s).
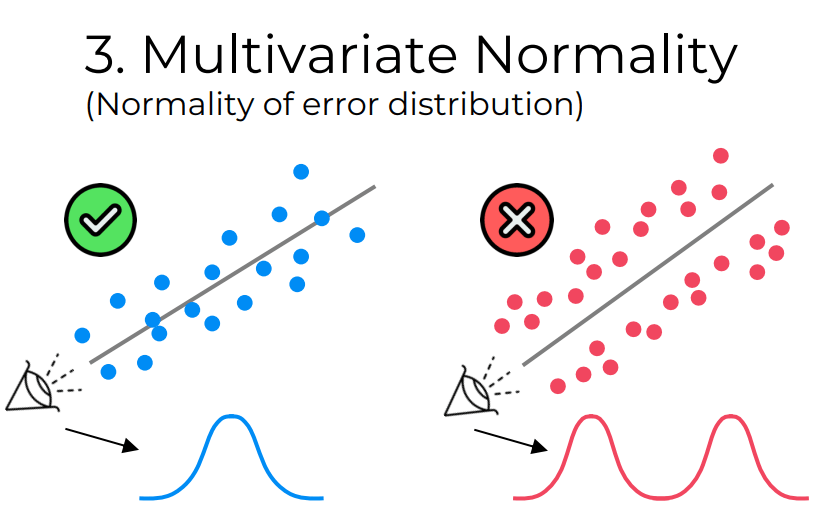
3. Multivariate Normality
The assumption of multivariate normality suggests that the residuals should follow a normal distribution. This assumption holds when the residuals have a symmetric, bell-shaped distribution around zero. It is important to check the normality assumption to ensure the accuracy of statistical inference.
While this assumption is not strictly necessary for large sample sizes, it becomes crucial for smaller datasets.
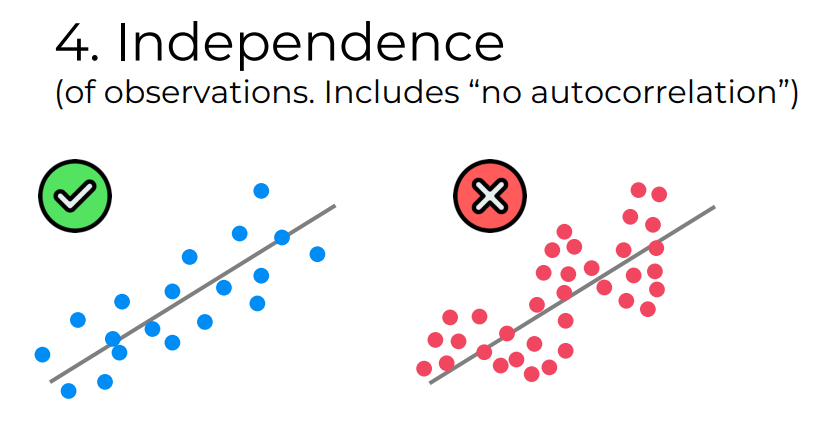
4. Independence
Independence assumes that the residuals are not correlated with each other. This means that the value of one residual should not provide any information about the value of another residual. The violation of this assumption can lead to unreliable parameter estimates.
5. Lack of Multicollinearity
Multicollinearity refers to a high correlation between independent variables in a regression model. This assumption assumes that there is little to no linear relationship between the independent variables. High multicollinearity can make it difficult to interpret the effects of individual variables and can lead to unstable regression coefficients.
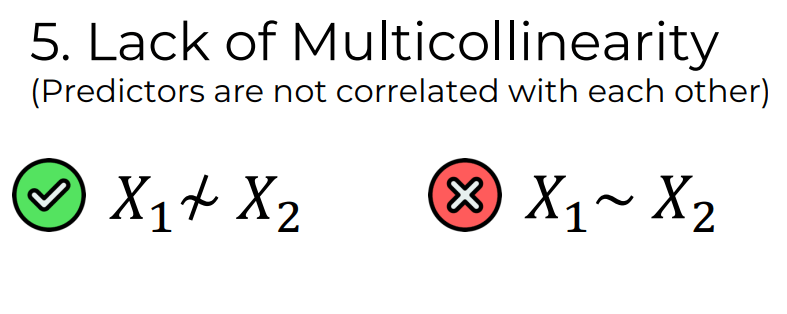
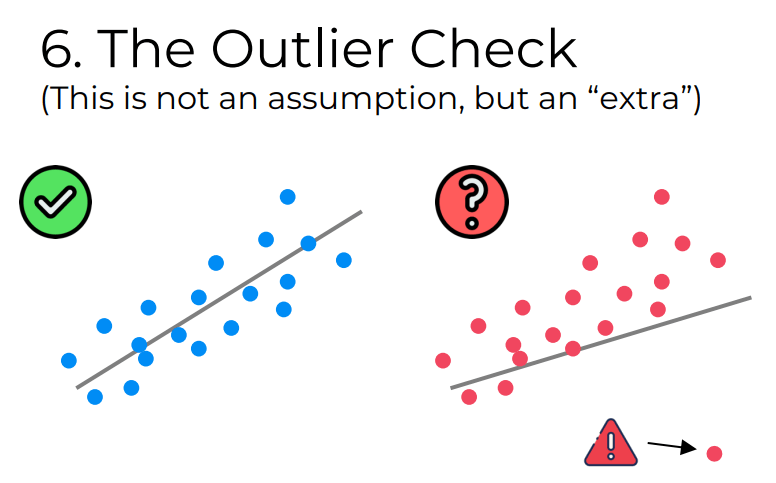
Outlier Check
Outliers are observations that deviate significantly from the overall pattern of the data. Identifying and handling outliers is essential as they can have a substantial impact on the results of a linear regression analysis. There are various techniques to detect outliers, such as graphical methods (e.g., scatter plots, box plots) or statistical tests (e.g., studentized residuals, Cook’s distance). Once identified, outliers can be addressed by either removing them or transforming the data to mitigate their influence on the analysis.
In conclusion, before performing a linear regression analysis, it is crucial to assess the assumptions of linearity, homoscedasticity, multivariate normality, independence, and lack of multicollinearity. Additionally, conducting an outlier check helps ensure the reliability of the regression model. By acknowledging and addressing these assumptions and outlier concerns, we can obtain more accurate and meaningful results from our linear regression analysis.
Photo Credits: Super Data Science

Leave a comment