While learning Salesforce, it’s important to start with its core building blocks. Lets break down three foundational concepts: Orgs, Objects, and Fields. Understanding these things will make everything much more sense.
What is an Org?
In Salesforce, an Org (Organization) is an instance of Salesforce. Think of it as the personal version of Salesforce that holds all your company’s data, modifications, and applications.
Key points about Orgs:
- Every company has its own Org.
- You can get a free Salesforce Developer Org to practice. Sign up here.
- Orgs can be Production, Sandbox or Developer Orgs.
What are Objects?
Objects are like database tables in Salesforce. They store the data in records, just like a spreadsheet in excel that stores rows of information. There are two main types of objects:
- Standard Objects
- Custom Objects
1. Standard Objects
Standard Objects are in-built objects that Salesforce provides out of the box. These objects covers the common business needs, so that we don’t have to build everything from scratch.
Examples of Standard Objects:
- Account
- Campaign
- Case
- Contact
- Lead
- Opportunity — etc
Standard Objects provide a solid foundation for core CRM functions like managing customer relationships, sales pipelines.
2. Custom Objects
Custom Objects are user-defined database tables that allows to store information which is unique to the organization. These custom objects are created by admin/developer team to track information.
How to identify a custom object ?
In Salesforce, all Custom objects have the suffix as __c at the end of their API name.
Examples of Custom Objects:
- Project__c
- Job_Application__c — etc
Standard Objects do not have a suffix at the end of their API.
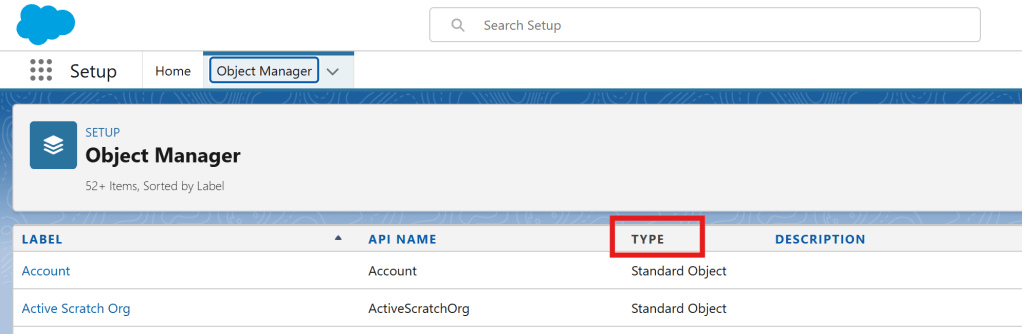
We can also check in the Object Manager to determine the type of the object.
In Setup -> Object Manager, we can see a list of objects. And it also shows a column for the Type.
What are Fields?
Fields are like the columns in the databse table, it defines what data we can store in the Object.
Similar to the objects, here also we have two different types of fields
- Standard Fields: Provided by Salesforce (like Name, Created Date).
- Custom Fields: We can add these to store specific info (e.g., “Customer Type”, “Subscription End Date”).
How They Work Together
Here’s how these pieces fit:
👉 Org → Its the entire Salesforce environment.
👉 Objects → Tables that hold data.
👉 Fields → Columns that define what data we can store for each record.
What’s Next?
In next blog, we’ll get even more hands-on by creating the first Custom Object from scratch, adding records, and exploring how data flows!
If you enjoyed this, leave a comment below! 🙌
Leave a comment